Navigating FAFSA and 529 Education Account Updates

Planning for college education costs is a complex, lengthy and likely, expensive endeavor. At first glance, the process seems simple; set aside money after a child is born, and then, after 18 years or so, use the funds saved to pay tuition. Unfortunately, laws, regulations, and the ever-increasing college tuition complicate the process. Recently, changes born out of the FAFSA (Free Application for Federal Student Aid) Simplification Act along with the SECURE 2.0 Act carry significant updates for Federal Student Aid along with funds saved within a 529 plan. We have highlighted a few of these recent updates to help navigate this changing landscape.
529 Account Changes
One of the benefits of a 529 account are that funds saved within this account grow tax-deferred and can be distributed tax-free when used for qualified education expenses. Qualified education expenses include tuition, room and board, books, computers, and student loan payments subject to a $10,000 lifetime limit.
The most recent change for 529 plans begins in 2024. If assets are not used and remain within the 529 account, there is now the option to roll 529 account funds to a Roth IRA account. This reduces the worry of having money trapped in 529 accounts, which is a common reason cited for not having established and funded a 529 account. The 529 assets can be rolled into a Roth account under a few requirements:
- The 529 account must have been open and owned for 15 years. Any contributions in the past 5 years are not eligible for rollover.
- The beneficiary must have an earned income up to the annual amount rolled into the Roth account. Annual rollover amounts are limited to the IRS maximum, currently $7,000 for 2024.
- The Roth account owner must also be the same as the beneficiary.
- A lifetime limit of $35,000.
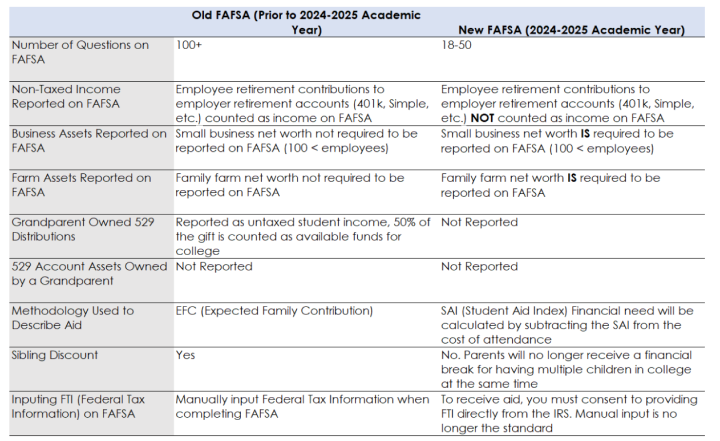
FAFSA Simplification Act
This Act will implement major FAFSA changes starting for the 2024-2025 academic year. Some of the most significant changes will be toward what income and assets will be reported on the FAFSA, which can increase or decrease aid, depending on the individual circumstances:
- Business owners with less than 100 employees must report the business net worth as an asset.
- For owners of family farms, the family farm’s net worth must be reported as an asset.
- Non-taxed income, such as employee contributions to employer retirement plans, will no longer count as income on the FAFSA.
- Distributions from a 529 account owned by a grandparent are no longer counted as income to the student.
- If divorced, the FAFSA is now to be filled out by the parent that provides the most financial support to the child rather than by the parent with majority custody.
Determining the most suitable approach to saving for college expenses is a highly personalized process influenced by financial goals, personal finances, and family dynamics. Initiating these conversations early and engaging in ongoing discussions is essential. The journey toward achieving educational funding goals is a marathon; much like saving toward a retirement goal. Heritage Wealth Architects can help navigate this process. We are experts and can create a plan for meeting family education goals and beyond.
Sources:
- FAFSA Simplification Act Changes for Implementation in 2024-25
- Schwab Article: 529 to Roth Rollover